Urinary Tract Infections for Women
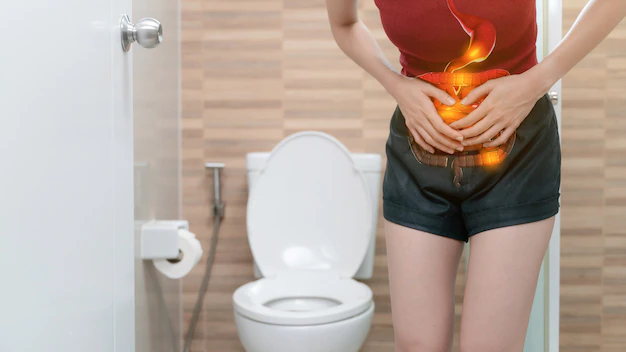
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common problem among women, with an estimated 50-60% of women experiencing at least one UTI in their lifetime. Here’s what you should know about UTIs:
- Causes: UTIs are caused by bacteria, most commonly E. coli, entering the urinary tract and causing an infection. This can happen when bacteria from the anus or vagina spread to the urethra and travel up to the bladder.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of a UTI may include a frequent urge to urinate, pain or burning during urination, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pelvic pain. Some women may also experience fever or chills.
- Risk factors: Women are more likely to develop UTIs due to the shorter length of their urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to travel to the bladder. Other risk factors include sexual activity, using certain types of contraceptives, and menopause.
- Diagnosis: A healthcare provider can diagnose a UTI by performing a urine culture to identify the bacteria causing the infection. They may also perform a physical exam to check for any signs of infection.
- Treatment: UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics. It’s important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished.
- Prevention: To prevent UTIs, it’s important to practice good hygiene habits, such as wiping from front to back after using the bathroom, urinating after sexual activity, and staying hydrated. Using cranberry supplements or drinking cranberry juice may also help to prevent UTIs.
If you suspect that you may have a UTI, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment. Left untreated, UTIs can lead to more serious infections and kidney damage. With prompt treatment, however, most UTIs can be easily managed and cleared up within a few days.
