Transrectal Ultrasound and Prostate Biopsy
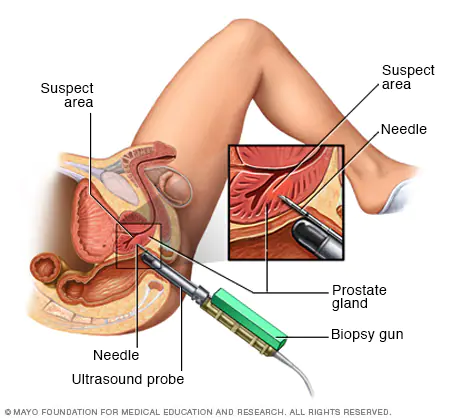
Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) and prostate biopsy are diagnostic tests used in the evaluation of prostate cancer.
TRUS uses sound waves to create images of the prostate gland. During the procedure, a small probe is inserted into the rectum and sound waves are used to create an image of the prostate gland. This test is commonly used to evaluate the size and shape of the prostate gland and to look for abnormalities.
Prostate biopsy involves the removal of a small tissue sample from the prostate gland for examination under a microscope. This procedure is typically performed following an abnormal PSA test or abnormal TRUS. During the biopsy, a needle is inserted through the rectum or through the area between the scrotum and anus to remove the tissue sample.
Prostate biopsy can be uncomfortable and may cause bleeding, infection, or other complications. However, it is an important diagnostic tool in the evaluation of prostate cancer and can provide valuable information about the presence and severity of the disease.
