Periodontal Disease
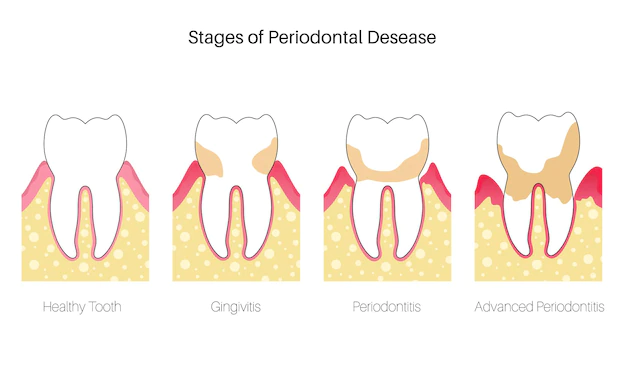
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a bacterial infection that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It is one of the most common dental problems, and if left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss. Here are some important things to know about periodontal disease:
- Causes: Periodontal disease is caused by bacteria that accumulate on the teeth and gums. These bacteria produce toxins that can damage the gums and other tissues in the mouth.
- Symptoms: The symptoms of periodontal disease can include swollen, tender, or bleeding gums, bad breath, loose teeth, and changes in the way teeth fit together when biting or chewing.
- Risk factors: Certain factors can increase your risk of developing periodontal disease, including smoking, poor oral hygiene, genetics, diabetes, and certain medications.
- Prevention: You can reduce your risk of developing periodontal disease by practicing good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing regularly, using an antiseptic mouthwash, and visiting your dentist for regular cleanings and check-ups.
- Treatment: The treatment for periodontal disease depends on the severity of the condition. In its early stages, the condition can often be treated with improved oral hygiene and professional cleanings. In more advanced cases, surgical interventions may be necessary.
If you think you may have periodontal disease, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible. Early detection and treatment can help prevent the condition from progressing and reduce the risk of tooth loss.
