Medical Treatments for Migraine Headaches
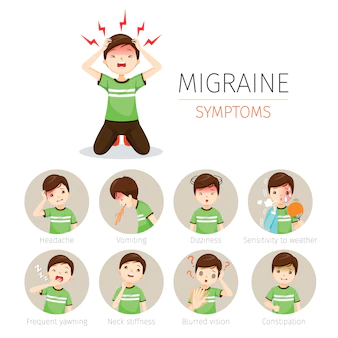
Migraine headaches are a type of headache that is often accompanied by symptoms such as nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances. They can be severe and disabling, and can last for hours or even days. There are several medical treatments available for migraines, and they can be divided into two main categories: acute treatments and preventive treatments.
Acute treatments are medications that are used to relieve the pain and other symptoms of a migraine attack. These medications work best if taken as soon as the migraine begins. Common acute treatments for migraines include:
- Triptans: Triptans are a class of drugs that work by narrowing blood vessels in the brain and reducing inflammation. They can be taken as tablets, nasal sprays, or injections, and are usually effective in relieving migraine pain within a few hours.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen can be effective in relieving the pain of a migraine attack. They work by reducing inflammation and pain.
- Acetaminophen: Acetaminophen can be effective in relieving the pain of a mild to moderate migraine attack. It works by blocking pain signals in the brain.
- Anti-nausea medications: Anti-nausea medications such as metoclopramide and prochlorperazine can be helpful in relieving the nausea and vomiting associated with migraines.
Preventive treatments are medications that are taken on a regular basis to reduce the frequency and severity of migraine attacks. They are usually recommended for people who experience migraines more than twice a month. Common preventive treatments for migraines include:
- Beta blockers: Beta blockers are medications that are commonly used to treat high blood pressure. They can also be effective in preventing migraines by reducing the frequency and severity of attacks.
- Antidepressants: Some antidepressant medications, such as amitriptyline and venlafaxine, have been shown to be effective in preventing migraines.
- Anticonvulsants: Anticonvulsant medications such as valproic acid and topiramate can be effective in preventing migraines. They work by reducing the hyperexcitability of neurons in the brain.
- Botox: Botox injections have been approved by the FDA for the prevention of chronic migraines. They are administered every 12 weeks and work by blocking the release of chemicals that cause pain.
It is important to note that not all migraine treatments work for everyone, and it may take some trial and error to find the right treatment plan. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to find the best treatment plan for each individual.
