Electrical Tests to Determine Back Pain
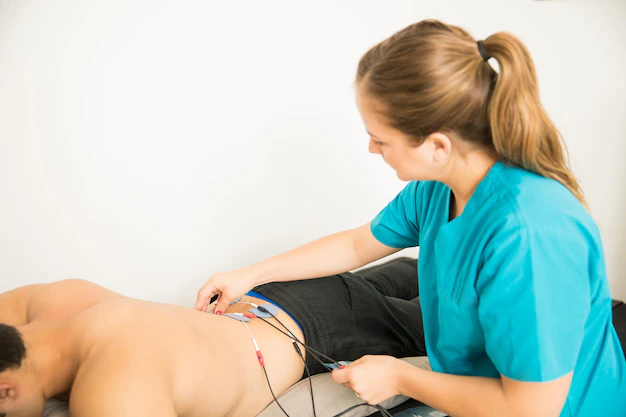
Electrical tests are not typically used to determine the cause of back pain, but they may be used to diagnose specific conditions that can cause back pain or related symptoms. Some examples of electrical tests that may be used include:
- Electromyography (EMG): This test measures the electrical activity of muscles and nerves. It can help determine if there is any nerve damage or muscle weakness present, which could be contributing to the patient’s back pain.
- Nerve Conduction Study (NCS): This test measures how well electrical signals are moving through the nerves. It can help determine if there is any nerve damage or if the nerves are being compressed, which could be causing the patient’s back pain.
- Somatosensory Evoked Potential (SEP) Test: This test measures the electrical signals produced by the sensory nerves in response to a stimulus. It can help diagnose conditions such as spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, or other nerve-related conditions that can cause back pain.
These tests are usually ordered by a doctor or specialist after a physical examination and other diagnostic tests have been performed. They can provide valuable information about the underlying cause of the patient’s back pain and help guide appropriate treatment.
