Cirrhosis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
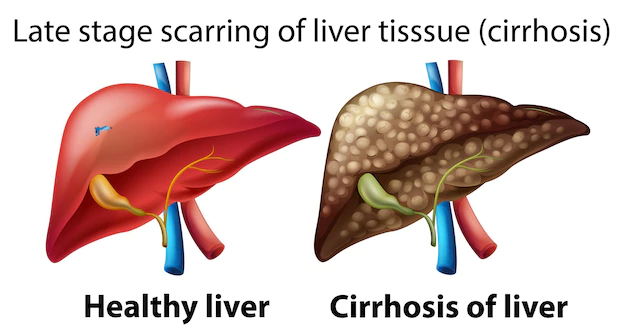
Cirrhosis is a condition in which the liver becomes scarred and damaged over time due to chronic liver disease, such as hepatitis or alcoholism. The scar tissue can cause the liver to lose its ability to function properly, leading to a range of symptoms and complications.
Symptoms of cirrhosis can include fatigue, weakness, jaundice, itching, abdominal pain, swelling in the legs and ankles, and confusion or difficulty thinking clearly.
Diagnosis of cirrhosis typically involves blood tests to check liver function, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI, and a liver biopsy, which involves taking a small sample of liver tissue for examination.
Treatment for cirrhosis depends on the underlying cause and the extent of liver damage. In some cases, lifestyle changes such as avoiding alcohol and eating a healthy diet can help slow the progression of the disease. Medications may also be prescribed to manage symptoms and complications.
In more severe cases, liver transplantation may be necessary. This involves replacing the damaged liver with a healthy liver from a donor. However, not everyone with cirrhosis is a candidate for a liver transplant, and the procedure carries its own risks and complications.
It’s important for individuals with liver disease to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their condition and prevent further damage to the liver. Regular monitoring, adherence to treatment plans, and lifestyle changes can all help improve outcomes for those with cirrhosis.
