Arrhythmias and Heart Disease
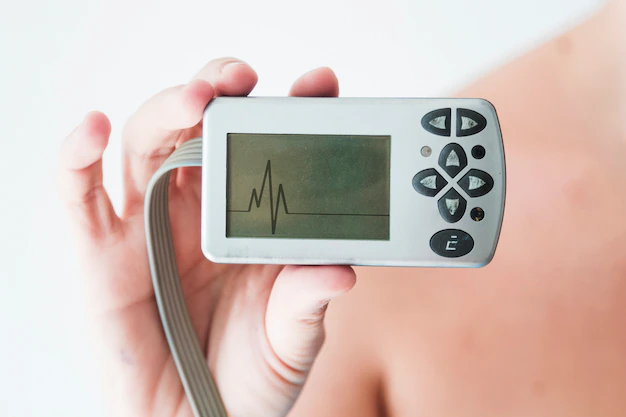
An arrhythmia is an abnormal heartbeat that can be too fast, too slow, or irregular. It occurs when the electrical signals that regulate the heartbeat do not function correctly, causing the heart to beat out of rhythm. Arrhythmias can be temporary or persistent and can range from mild to life-threatening.
There are several types of arrhythmias, including:
- Atrial fibrillation (AFib): This is the most common type of arrhythmia, where the heart’s upper chambers (atria) beat irregularly and too fast.
- Bradycardia: This is when the heart rate is slower than normal.
- Tachycardia: This is when the heart rate is faster than normal.
- Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs): This is when the heart beats earlier than normal.
- Ventricular fibrillation (VFib): This is a life-threatening arrhythmia where the heart’s lower chambers (ventricles) quiver and cannot pump blood.
Arrhythmias can occur in people with and without heart disease. However, several factors can increase the risk of developing arrhythmias, including:
- Age
- Family history of arrhythmias
- Coronary artery disease or heart attack
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Heart valve problems
- Hyperthyroidism
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol or caffeine consumption
Symptoms of arrhythmias may include palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, fainting, chest pain, or discomfort. However, some people may have no symptoms at all.
Diagnosis of arrhythmias involves a physical exam, an electrocardiogram (ECG), and other tests like a Holter monitor, event monitor, or echocardiogram. Treatment options for arrhythmias depend on the type and severity of the arrhythmia and may include lifestyle changes, medications, medical procedures like cardioversion or catheter ablation, or the insertion of a pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) device.
It is essential to seek medical attention if you suspect that you have an arrhythmia. Your doctor can provide an accurate diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan to help manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
