Age Spots
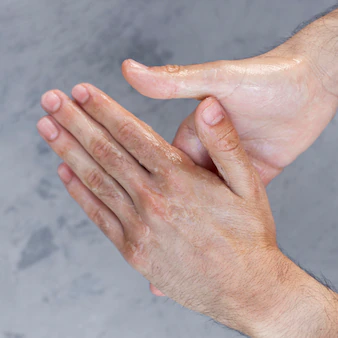
Age spots, also known as liver spots or solar lentigines, are flat, brown, or black spots that commonly appear on the skin as a result of exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. They typically appear on areas of the skin that receive the most sun exposure, such as the face, hands, arms, and shoulders.
Age spots are most commonly seen in adults over the age of 50, although they can occur in younger individuals as well. While age spots are generally harmless, they can be a cosmetic concern for some people, as they can make the skin appear older or uneven.
Treatment for age spots typically involves the use of topical medications, such as hydroquinone or retinoids, which work to lighten the skin and fade the appearance of age spots over time. In some cases, laser or intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy may be recommended to help remove age spots.
Prevention of age spots involves protecting the skin from sun exposure by wearing protective clothing and using sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. Regular skin exams can also help to detect any new or changing spots on the skin that may require medical attention.
