Acute Treatment of an Ischemic Stroke
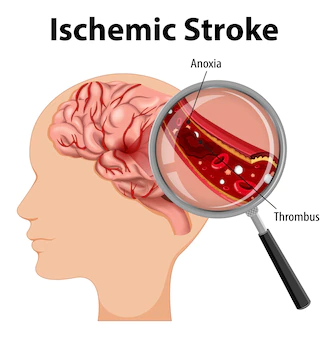
Acute treatment of an ischemic stroke typically involves two main approaches: thrombolysis and mechanical thrombectomy.
Thrombolysis involves administering a medication called tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) to dissolve the clot causing the stroke. This medication must be given within a certain time frame after the onset of symptoms and requires careful monitoring to prevent bleeding complications.
Mechanical thrombectomy involves using a catheter to physically remove the clot from the blocked blood vessel. This approach is often used when thrombolysis is not feasible or effective.
In addition to these treatments, patients with an ischemic stroke may receive other supportive measures such as blood pressure control, blood sugar management, and treatment for any underlying medical conditions that contributed to the stroke.
It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a stroke, as time is a critical factor in determining the success of treatment and reducing the risk of long-term complications.
