Acute Bronchitis
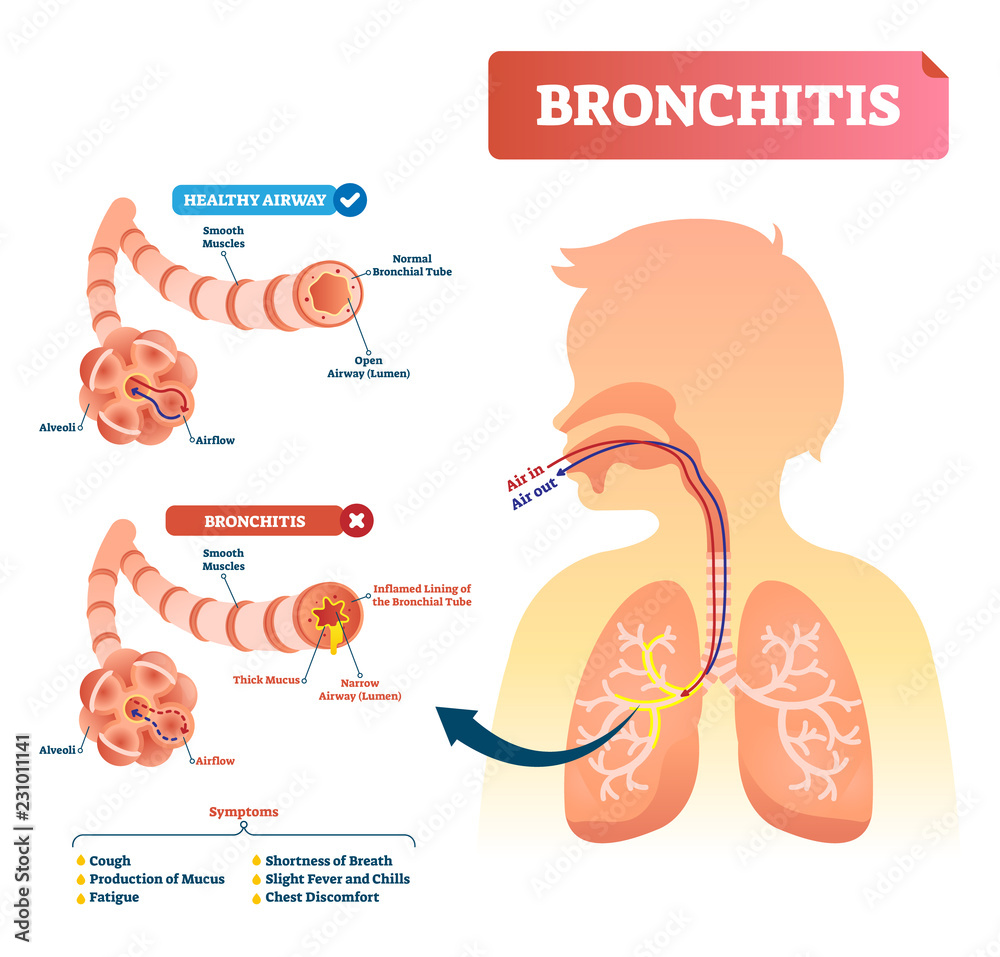
Acute bronchitis is a common respiratory condition that affects the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the lungs. It is typically caused by a viral infection and can be accompanied by symptoms such as cough, chest congestion, and difficulty breathing.
Symptoms of acute bronchitis usually develop within a few days of exposure to a virus or other irritant, such as cigarette smoke or air pollution. The most common symptom is a persistent cough, which may be accompanied by yellow or green mucus. Other symptoms may include:
- Chest congestion or tightness
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
- Sore throat or hoarseness
- Fatigue or weakness
- Low-grade fever or chills
Most cases of acute bronchitis resolve on their own within a few weeks, without the need for medical treatment. However, over-the-counter medications such as cough suppressants or expectorants may help relieve symptoms. If the symptoms are severe or last longer than a few weeks, or if there is a high fever, chest pain, or difficulty breathing, it is important to seek medical attention.
To prevent acute bronchitis, it is important to practice good respiratory hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing. Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke and air pollutants can also help reduce the risk of developing acute bronchitis.
In conclusion, acute bronchitis is a common respiratory condition that is usually caused by a viral infection. Although it can be uncomfortable, most cases resolve on their own within a few weeks, and over-the-counter medications can help relieve symptoms. It is important to seek medical attention if symptoms are severe or last longer than a few weeks.
