Symptoms of Menopause
Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s reproductive years. It is defined as the permanent cessation of menstrual periods for at least 12 months, and typically occurs in women between the ages of 45 and 55. During menopause, the body’s production of the hormones estrogen and progesterone declines, leading to a range of symptoms.
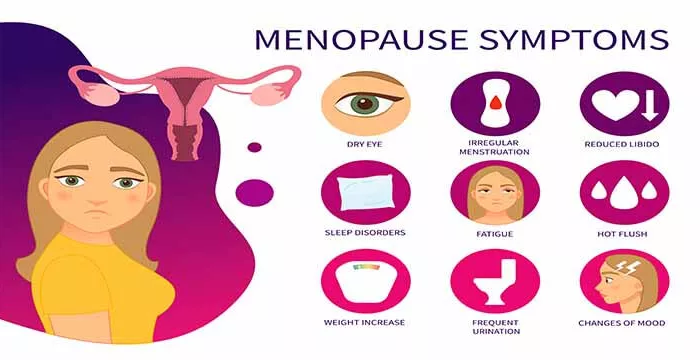
Here are some of the most common symptoms of menopause:
- Hot flashes: Hot flashes are sudden, intense sensations of heat that can cause sweating, flushing, and palpitations. They can occur during the day or night and may last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes.
- Night sweats: Night sweats are episodes of sweating that occur during sleep, often accompanied by chills and waking up feeling hot and clammy.
- Vaginal dryness and discomfort during sex: Menopause can cause changes in vaginal tissue that lead to dryness, itching, and discomfort during sex.
- Mood changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels can lead to mood changes such as irritability, anxiety, depression, and mood swings.
- Sleep disturbances: Menopause can cause sleep disturbances such as insomnia, waking up frequently during the night, and difficulty falling asleep.
- Decreased libido and sexual function: Changes in hormone levels can also lead to a decrease in libido and sexual function, including decreased sexual desire, difficulty achieving orgasm, and vaginal dryness.
- Urinary problems: Menopause can lead to urinary problems such as incontinence, urinary tract infections, and an increased urge to urinate.
- Changes in body composition: Menopause can lead to changes in body composition such as weight gain, particularly around the waist, and a loss of muscle mass.
While menopause is a natural process, the symptoms can be uncomfortable and disruptive to daily life. It’s important for women to speak with their healthcare provider about their symptoms and to develop a management plan that works for them.
