Pneumonia
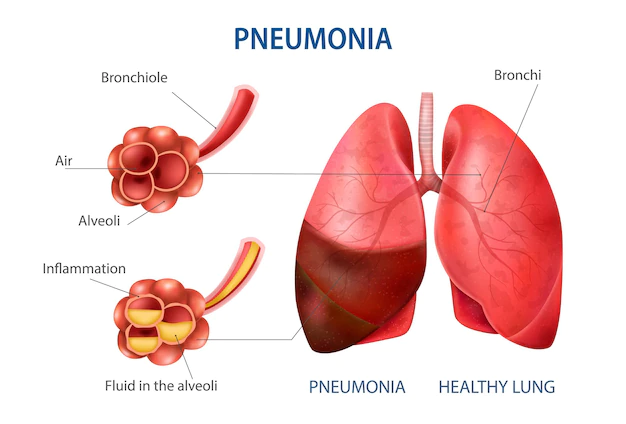
Pneumonia is a serious respiratory infection that can affect one or both lungs. It is typically caused by bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms and can be life-threatening, especially in older adults and people with weakened immune systems.
The symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Fever and chills
- Cough, which may produce phlegm or pus
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Chest pain, especially when coughing or breathing deeply
- Fatigue or weakness
- Confusion, particularly in older adults
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications.
Pneumonia can be diagnosed through a physical exam, chest X-ray, blood tests, and other diagnostic tests. Treatment typically involves antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia or antiviral medication for viral pneumonia, as well as supportive care to manage symptoms, such as fever and cough.
Prevention of pneumonia includes good respiratory hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing. Vaccines are also available to prevent some types of pneumonia, such as pneumococcal and influenza.
In conclusion, pneumonia is a serious respiratory infection that requires prompt medical attention. Symptoms can vary, but may include fever, cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue. Treatment involves antibiotics or antiviral medication, as well as supportive care to manage symptoms. Good respiratory hygiene and vaccination can help prevent pneumonia.
