Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
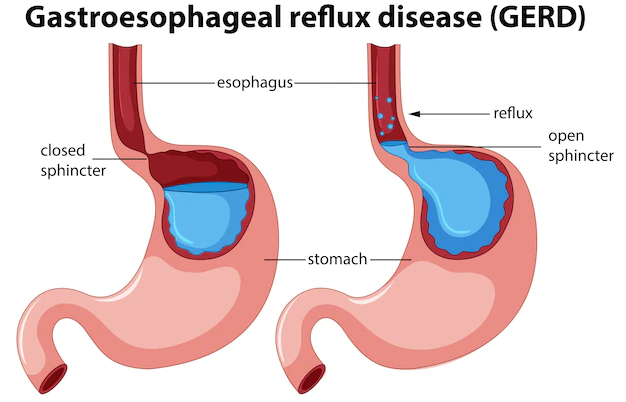
The treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) may involve lifestyle changes, medications, or surgery.
Lifestyle changes that may be recommended include:
- Avoiding trigger foods that worsen symptoms, such as spicy or acidic foods
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals instead of large meals
- Avoiding lying down for at least two to three hours after eating
- Elevating the head of the bed by six to eight inches to prevent acid from flowing into the esophagus at night
- Losing weight if overweight or obese
Medications that may be prescribed to treat GERD include:
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) such as omeprazole, esomeprazole, lansoprazole, or pantoprazole, which reduce the amount of acid produced by the stomach
- H2 blockers such as ranitidine, famotidine, or cimetidine, which also reduce acid production
- Antacids such as Tums, Rolaids, or Maalox, which neutralize stomach acid
- Prokinetics such as metoclopramide, which help the stomach empty more quickly and reduce the amount of acid produced
Surgery may be considered if lifestyle changes and medications do not provide sufficient relief. The most common surgical procedure for GERD is called fundoplication, which involves wrapping a part of the stomach around the lower esophageal sphincter to strengthen it and prevent acid reflux.
