How Plaque Buildup Can Cause Heart Attacks
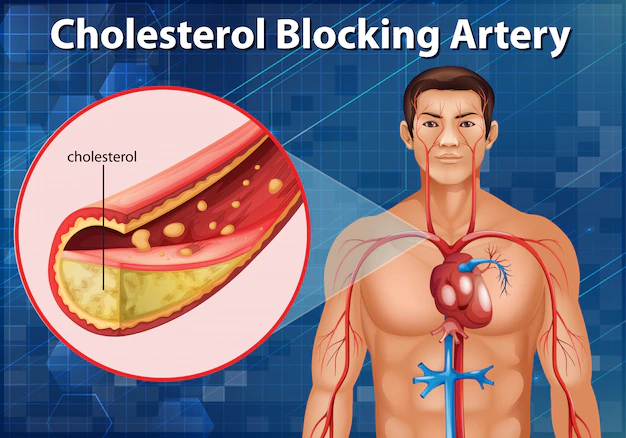
Plaque buildup, also known as atherosclerosis, is a condition in which cholesterol and other substances build up on the walls of arteries over time. This buildup can narrow the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart and other organs. Over time, plaque buildup can lead to the development of heart disease and increase the risk of heart attack.
When plaque buildup occurs in the arteries that supply blood to the heart, it can lead to coronary artery disease. Over time, the plaque can grow and harden, narrowing the arteries and reducing blood flow to the heart. In some cases, a blood clot can form on the plaque, completely blocking the artery and causing a heart attack.
Heart attacks occur when the blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, often due to a blood clot that forms on top of plaque buildup. Without blood and oxygen, the heart muscle can be damaged or die. The symptoms of a heart attack can include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, nausea or vomiting, and lightheadedness.Risk factors for plaque buildup and heart disease include high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and a family history of heart disease. Lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, not smoking, and managing other health conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes can help reduce the risk of plaque buildup and heart disease.
In conclusion, plaque buildup in the arteries can cause heart attacks by narrowing the arteries and reducing blood flow to the heart. When a blood clot forms on the plaque, it can completely block the artery and cause a heart attack. By managing risk factors and making lifestyle changes, it’s possible to reduce the risk of plaque buildup and heart disease.
