Muscles that Support the Back
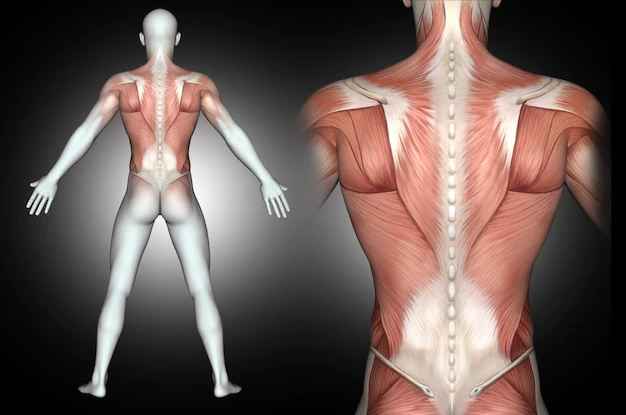
The back is a complex structure made up of bones, muscles, ligaments, and nerves that work together to provide support, stability, and flexibility to the body. The following are some of the muscles that support the back:
- Erector Spinae: This is a group of muscles that run along the length of the spine, from the pelvis to the skull. They are responsible for maintaining the upright posture of the body and helping to bend and rotate the spine.
- Multifidus: These are a group of small muscles that run alongside the spine and help to stabilize it during movement.
- Quadratus Lumborum: This muscle runs from the pelvis to the lower ribs and helps to stabilize the lumbar spine and pelvis during movement.
- Gluteus Maximus: This is the largest muscle in the body and is responsible for extending the hip and helping to support the lower back.
- Hamstrings: These are a group of muscles that run along the back of the thigh and attach to the pelvis and lower leg. They help to support the lower back and stabilize the pelvis during movement.
- Abdominal Muscles: The abdominal muscles, including the rectus abdominis and obliques, play an important role in supporting the lower back and stabilizing the pelvis.
- Latissimus Dorsi: This is a large muscle that runs from the spine to the upper arm and is responsible for extending the shoulder and helping to stabilize the back.
- Trapezius: This muscle runs from the base of the skull to the upper back and shoulders and helps to stabilize the scapula (shoulder blade) during movement.
It is important to maintain the strength and flexibility of these muscles to prevent and manage back pain. Exercises that target these muscles can help to improve posture, reduce pain, and prevent further injury.
