Stroke Overview
Here is an overview of strokes, the fifth leading cause of death.
Types of Strokes
Learn how to differentiate the different types of strokes.
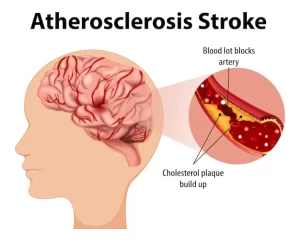
How a Stroke Damages the Brain
Find out how a stroke causes brain damage.

Stroke Risk Factors that Cannot Be Changed
Some risk factors for strokes cannot be changed, like family history, but they can be monitored.

Stroke Risk Factors that Can Be Changed
Learn how to take control of your stroke risk factors.

Stroke Signs and Risk Factors for Women
Strokes are a deadly condition that affect more women than men. Learn how to identify a stroke and get quick treatment.

Stroke Symptoms and Actions To Take
Learn to identify the symptoms of a stroke in order to take immediate action in an emergency.

Stroke Prevention
Learn how to prevent strokes using lifestyle changes, medication, and surgery.

Thirteen Key Facts About Strokes
Here are things you may not know about strokes, some of which may save a life.
Diagnosis of a Stroke
Find out how a stroke is diagnosed in the hospital.
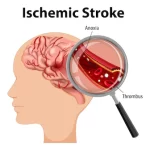
Acute Treatment of an Ischemic Stroke
How an ischemic stroke is treated in the hospital depends on many factors, including the type of stroke and how long the symptoms have been occurring.
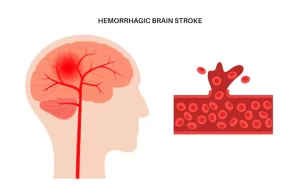
Treatment of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Emergency treatment of a hemorrhagic stroke focuses on controlling bleeding, blood pressure, and pressure in the brain.

Antiplatelet Medications to Treat Heart Attack and
Heart Disease
When your doctor wants to reduce your risk of blood clots, he or she may prescribe an antiplatelet drug.
Heart Disease
Impact Stroke Has on the Brain
Strokes can cause different types of brain damage depending on where in the brain they occur.
Impact of Stroke on Long-Term Health
Having a stroke can greatly impact your long-term health.

Depression After a Stroke
Depression is common after a stroke. Find out how to identify and treat this difficult mental health condition.

Stroke Rehabilitation
Here is what to expect from rehabilitation after a stroke.
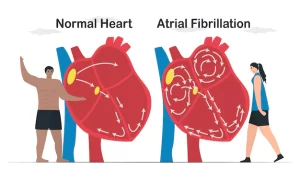
Overview of Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common condition that affects the heart. It causes a fast, irregular, and chaotic heartbeat. Over time, the presence of AF can lead to blood clots and stroke.

Atrial Fibrillation: Symptoms and Causes
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF) can vary from person to person. A long list of circumstances and conditions is linked to AF.

Atrial Fibrillation: Diagnosis
Learn how atrial fibrillation is diagnosed.
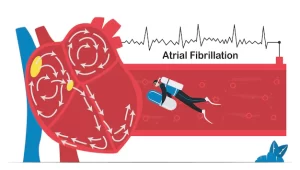
Atrial Fibrillation: Making Treatment Decisions
The three treatment goals for AF are preventing stroke, improving quality of life by reducing symptoms, and preserving ventricular function.

Atrial Fibrillation: Getting a Second Opinion
When it comes to atrial fibrillation, seeking another opinion is a smart move.

Who Can Benefit from Anticoagulation Therapy?
Find out if your risk of stroke due to atrial fibrillation warrants daily medication with anticoagulants.
Anticoagulants: Treatments for Atrial Fibrillation
Why use anticoagulant medications (blood thinners) to treat atrial fibrillation and stroke? Find out more.

Suppressing Atrial Fibrillation Symptoms: Rate Control
To reduce AF symptoms, rate control (lowering the heart rate to normal levels), is just as effective and maybe safer than rhythm control (restoring a normal rhythm).

Rate Control Medications for Suppressing Atrial
Fibrillation Symptoms
Beta-blockers and certain calcium-channel blockers are the mainstays of heart rate-control therapy. The goal is to lower the resting heart rate and maintain it below 100 beats per minute (bpm).
Fibrillation Symptoms
Rate Control for Atrial Fibrillation Catheter Ablation
of the AV Node
One way to achieve heart rate control for atrial fibrillation (AF) is catheter ablation of the AV node.
of the AV Node
Suppressing Atrial Fibrillation Symptoms: Rhythm Control
Rhythm control is often recommended for patients with AF. The strategy: cardioversion returns the heart to normal sinus rhythm, and antiarrhythmic medication keeps it there.

Should You Start Antiarrhythmic Drug Therapy for Your
Atrial Fibrillation?
If you’re thinking about starting antiarrhythmic medication, here is a rundown of the risks and benefits.
Atrial Fibrillation?

